How to Calculate Intrinsic Value: Step-by-Step Guide for Investors
Share this article
“Price is what you pay. Value is what you get.”
– Warren Buffett
For investors, calculating a company’s intrinsic value is like having a financial compass. It helps you determine whether a stock is undervalued (a bargain) or overvalued (a trap). While the concept is simple—what is the true worth of a business?—the execution requires discipline, data, and a systematic approach.
In this guide, we’ll break down the key methods to calculate intrinsic value, highlight common pitfalls, and show you how tools like the ViA Atlas Case Study Membership streamline the process for investors like you.
Why Intrinsic Value Matters
Intrinsic value represents the true economic worth of a company, based on its ability to generate cash flows, assets, and growth potential. Unlike market price—which fluctuates daily due to sentiment—intrinsic value focuses on fundamentals.
Key benefits of mastering intrinsic value:
- Avoid overpaying for hype-driven stocks.
- Identify undervalued opportunities with a margin of safety.
- Build a portfolio grounded in long-term business performance.
3 Core Methods to Calculate Intrinsic Value
1. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
The gold standard for intrinsic valuation, DCF estimates the present value of a company’s future cash flows.
Formula:
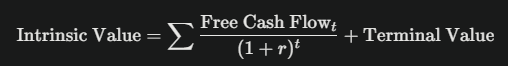
- Forecast Free Cash Flows (FCF): Project FCF for 5–10 years.
- Determine Discount Rate (WACC): Use the company’s weighted average cost of capital (typically 8–12%).
- Calculate Terminal Value: Estimate value beyond the forecast period (e.g., perpetual growth model).
- Sum and Discount: Add discounted FCF and terminal value.
Example:
If a company’s FCF is $100M annually, growing at 3% with a 10% discount rate, its intrinsic value would be ~$1.5B.
2. Dividend Discount Model (DDM)
Best for mature, dividend-paying companies.
Formula:

Steps:
1. Estimate Dividends: Use historical payouts and growth rates.
2. Apply Discount Rate: Reflect the risk of the investment (often 7–10%).
Example: A stock paying $4/year in dividends, growing at 2% annually, with a 9% discount rate, has an intrinsic value of ~$57/share.
3. Asset-Based Valuation
Calculates Net Asset Value (NAV) by subtracting liabilities from assets.
Formula:
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Overlooking the Margin of Safety
Buying a stock at its exact intrinsic value offers no buffer for errors. Legendary investor Benjamin Graham recommended purchasing stocks at ≤⅔ of intrinsic value to protect against unforeseen risks.
2. Overly Optimistic Growth Assumptions
Projecting 20% annual growth for a slow-moving industry (e.g., utilities) leads to inflated valuations. Base forecasts on historical averages and industry trends.
3. Ignoring Debt and Liabilities
A company with high debt may seem cheap on P/E but risky on intrinsic value. Always factor in balance sheet health.
Simplify Your Analysis with the ViA Atlas Case Study Membership
Calculating intrinsic value manually is time-consuming. The ViA Atlas Case Study Membership automates the heavy lifting:
- Pre-Vetted Companies: Access a curated list of undervalued stocks with detailed DCF models.
- Expert-Built Templates: Plug in numbers to auto-calculate intrinsic value.
- Margin of Safety Filters: Screen for stocks trading at 30%+ below fair value.
Real-World Example: Zhen Hong, A ViA Atlas member went from 4% per annum ROI to 20% per annum ROI just by following the Case Studies in our IV Directory.
Join Our Free Webinar: Step-By-Step Company Analysis of a Good Growth US-Listed Company
Want to see how it works? Join Cayden Chang, founder of Value Investing Academy, for a live webinar:
What You’ll Learn:
- A deep dive into a fast-growth company case study.
- What are the key financial metrics when evaluating whether a stock has strong growth potential.
- Step-by-step guide on how to apply value investing methodology on real-world companies.
- Learn the exact criteria that successful investors use to evaluate a company
- How to determine the intrinsic value of a stock so you'll know exactly when to enter or exit the market.
- How ViA Atlas Intrinsic Value (IV) Directory can get you started on building your own portfolio of superhero stocks, even for busy professionals without much time to spare
👉 Reserve Your Spot Now
Key Takeaways
- DCF is King: Focus on cash flows, not headlines
- Margin of Safety is Non-Negotiable: Always buy below intrinsic value
- Tools Save Time: Use the ViA Atlas to skip hours of manual work
By mastering intrinsic value, you will invest with confidence - not guesswork.
P.S. The market won’t wait. Claim your free webinar seat today.
How to Apply a Fundamental-First Approach to Investing
Presented by Cayden Chang
Founder of Value Investing Academy and Award-Winning International Speaker, Lifelong Learner Award 2008, Personal Brand Award 2017, 2025 Spirit of Enterprise Honouree
You will learn:
- How to navigate market uncertainty amidst geopolitical tensions and market uncertainty
- How can all-weather portfolio of stocks, bonds, and ETFs can help you stay calm and thrive no matter the market direction.
- How Cash-Flow Options Strategies (CFOS), modelled after Warren Buffett's principles of Value Investing can help you cope with market uncertainty
- How ViA Atlas could help you strengthen your portfolio and streamline your decision-making process
- Actionable & Duplicable Step-By-Step Value Investing Framework on identifying high-quality resilent companies
Click the button below to reserve your spot now.
Suitable For
Solutions For
Mind Kinesis Investments Pte Ltd. All Rights Reserved.


